
"Physical frailty may exacerbate the behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia (BSPD) in patients with Alzheimer disease, and also increase caregiver burden, per study data published in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry."
Posts published in “Research”
"Alzheimer's-affected brains are riddled with so-called amyloid plaques: protein aggregates consisting mainly of amyloid-β. However, this amyloid-β is a fragment produced from a precursor protein whose normal function has remained enigmatic for decades. A team of scientists at VIB and KU Leuven led by professors Joris de Wit and Bart De Strooper has now uncovered that this amyloid precursor protein modulates neuronal signal transmission through binding to a specific receptor. Modulating this receptor could potentially help treat Alzheimer's or other brain diseases. The results are published in Science."

"New research, published in the journal Nature Genetics, identifies new genetic risk factors for Alzheimer's disease. It also uncovers novel biological mechanisms that may lead to this neurodegenerative condition."

"Poor sleep is a hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease. People with the disease tend to wake up tired, and their nights become even less refreshing as memory loss and other symptoms worsen. But how and why restless nights are linked to Alzheimer’s disease is not fully understood."
"Certain inherited genetic mutations lead to Alzheimer’s disease (AD), but they are relatively rare. A recent study from my laboratory, however, shows that gene alterations that are not passed along by one’s parents may also play a key role in triggering the disease. This happens as a result of a process that occurs in the cell nucleus, known as gene recombination (GR), which can make changes to the DNA “blueprint” in human neurons."
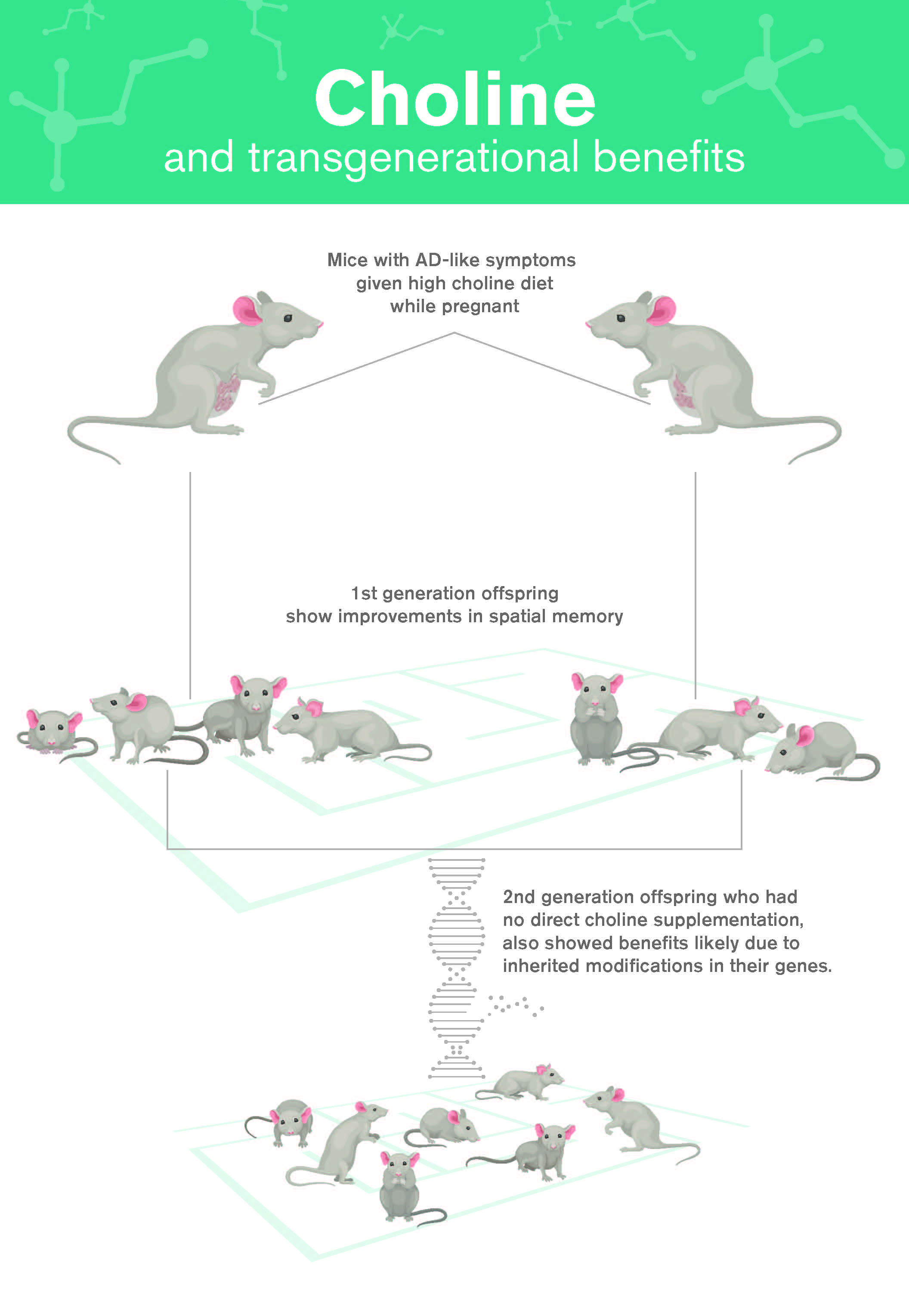
"In a new study, researchers at the Biodesign Institute explore a safe and simple treatment for one of the most devastating and perplexing afflictions: Alzheimer's disease. Lead authors Ramon Velazquez and Salvatore Oddo, along with their colleagues in the ASU-Banner Neurodegenerative Disease Research Center, investigated the effects of choline, an important nutrient that may hold promise in the war against the memory-stealing disorder. Mice with Alzheimer's-like symptoms receiving supplemental levels of choline in the womb improved their spatial memory. "
"According to a large worldwide study, the hormone that is produced in the body during exercise called irisin, can prevent and delay the onset of mental faculty decline and Alzheimer's disease. The results of the study were published in the latest issue of the journal Nature Medicine."

"Scientists have found a biological clue that could help explain why African-Americans appear to be more vulnerable than white Americans to Alzheimer's disease. A study of 1,255 people, both black and white, found that cerebrospinal fluid from African-Americans tended to contain lower levels of a substance associated with Alzheimer's, researchers report Monday in the journal JAMA Neurology."
"Alcohol use has been identified as a risk factor for dementia and cognitive decline. However, some patterns of drinking have been associated with beneficial effects."
"What do sedatives, general anesthetics, anti-anxiety drugs, alcohol, numerous recreational drugs, and allopregnanolone, a neurosteroid being tested in Alzheimer’s trials, have in common? They all tweak the activity of GABA-A receptors."
